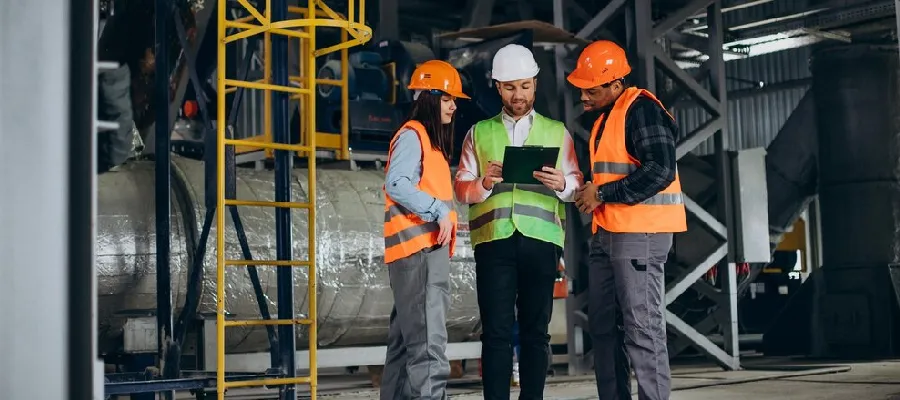
Commonly asked Questions and Answers Related to Magnetic Particle Testing (MT)
Here are some of the commonly asked questions and their answers for magnetic particle testing method. For details about our NDT courses visit our website at Palium Skills
Interview Questions and Answers Related to Magnetic Particle Testing (MT)
- What is Magnetic Particle Testing (MT)?
Ans: MT is a non-destructive testing method used to detect surface and near-surface flaws in ferromagnetic materials.
- How does MT work?
Ans: A magnetic field is applied to the material, and iron particles are applied to the surface. They accumulate at areas with magnetic flux leakage, indicating the presence of a flaw.
- What are the two types of magnetic particles used in MT?
Ans: Dry particles and wet particles.
- What is the purpose of applying a magnetic field during MT?
Ans: To identify flaws by inducing magnetic flux leakage at the defect locations.
- Explain the difference between longitudinal and circular magnetization.
Ans: Longitudinal magnetization runs parallel to the length of the part, while circular magnetization runs around the circumference.
- What are the essential components of a magnetic particle testing equipment setup?
Ans: Magnetizing equipment, magnetic particles, and a means of indication (e.g., developer).
- What are the advantages of using a yoke in MT?
Ans: Portable, easy to use, and effective for inspecting irregularly shaped parts.
- When is the prods method preferred over the yoke method?
Ans: When inspecting small, complex, or hard-to-reach areas.
- What is the purpose of a magnetic field indicator?
Ans: To verify that the specified magnetic field strength is applied during testing.
- Why is it important to demagnetize a part after testing?
Ans: To prevent residual magnetism, which could interfere with the part’s functionality.
- What are the steps involved in the MT inspection process?
Ans: Cleaning, magnetization, application of magnetic particles, interpretation, repeat inspection in the perpendicular direction, and demagnetization.
- How is the sensitivity of an MT inspection increased?
Ans: By using smaller particle size, increasing the magnetic field strength, and improving the inspection environment.
- Explain the purpose of the black light in MT.
Ans: Used in fluorescent magnetic particle testing to enhance visibility of indications.
- What is the purpose of the developer in MT?
Ans: It helps to draw out and highlight the indications formed by the magnetic particles.
- What factors can affect the visibility of indications in MT?
Ans: Lighting conditions, particle size, and the type of magnetic particle used.
- Why is it important to follow safety procedures in MT?
Ans: To protect personnel from potential hazards associated with magnetic fields and equipment.
- What standards govern magnetic particle testing?
Ans: ASTM E1444, ASME Section V, and ISO 9934.
- How can you ensure compliance with MT standards during an inspection?
Ans: Regularly calibrate equipment, follow proper procedures, and maintain detailed inspection records.
- What are the safety precautions when working with magnetic fields in MT?
Ans: Use personal protective equipment, establish restricted areas, and follow demagnetization procedures.
- Explain the importance of training and certification in MT.
Ans: Ensures that personnel are competent, knowledgeable, and can perform tests accurately.
- What types of defects can be detected using MT?
Ans: Surface cracks, seams, laps, and other discontinuities that are open to the surface.
- How do you differentiate between a crack and a scratch using MT?
Ans: Cracks will produce indications with a characteristic pattern, while scratches will not.
- What factors can affect the shape and size of indications in MT?
Ans: The orientation of the defect, the type of magnetic field, and the part’s geometry.
- Explain the concept of magnetic particle mobility in relation to indication interpretation.
Ans: The ability of magnetic particles to move and accumulate at defect locations, making indications visible.
- What is a false indication in MT, and how can it be minimized?
Ans: A non-relevant indication. Minimized by proper cleaning and careful interpretation.
- Describe a scenario where residual magnetism became a problem in MT.
Ans: Discuss a case where parts retained magnetism after testing, causing issues in subsequent processes.
- How would you handle a situation where indications are unclear during an MT inspection?
Ans: Reevaluate the inspection process, consider retesting, and consult with experienced personnel.
- Discuss a case where a non-magnetic particle was mistaken for a defect during MT.
Ans: Highlight the importance of understanding the materials and potential contaminants.
- Explain how you would troubleshoot equipment issues during an MT inspection.
Ans: Check for power supply issues, examine cables, and ensure proper calibration.
- Describe a situation where personal protective equipment played a crucial role in an MT inspection.
Ans: Emphasize the importance of wearing appropriate gear to prevent exposure to magnetic fields.
- What advancements have been made in magnetic particle testing technology recently?
Ans: Discuss any developments in equipment, materials, or inspection processes.
- How can digital imaging and automation enhance MT inspections?
Ans: Faster data analysis, increased accuracy, and improved documentation.
- Explain the role of artificial intelligence in the future of MT.
Ans: AI can assist in defect recognition, data analysis, and decision-making.
- How might the integration of augmented reality impact the training of MT inspectors?
Ans: AR can provide real-time guidance, enhancing the learning experience for trainees.
- Discuss any environmental considerations in the use of magnetic particles for testing.
Ans: Considerations related to waste disposal, particle reuse, and environmental impact.
- What are the limitations of MT?
Ans: Limited to ferromagnetic materials, surface defects, and requires a clean surface.
- Explain the difference between continuous and residual magnetization.
Ans: Continuous magnetization involves applying a magnetic field during the entire inspection, while residual magnetization remains after the field is removed.
- How does temperature affect the magnetic particle inspection process?
Ans: Extreme temperatures can impact the performance of magnetic particles and equipment.
- What are the key considerations for selecting the appropriate magnetic particle testing method for a specific application?
Ans: Material type, part geometry, defect type, and inspection environment.
- Discuss the importance of documentation in the MT process.
Ans: Documentation is essential for traceability, quality control, and meeting regulatory requirements.
If you have any questions or queries on NDT Training for VT, RT, UT, MPT etc. then reach out to us through the contact form on our website – www.paliumskills.com